UNIT-3
- Distinguish international marketing and Domestic marketing?
Marketing is defined as the set of activities which are undertaken by the companies to provide satisfaction to the customers through value addition and making good relations with them, to increase their brand value. It identifies and converts needs into products and services, so as to satisfy their wants.
There are two types of marketing namely, domestic and international marketing. Domestic marketing is when commercialization of goods and services are limited to the home country only. On the other hand, International marketing, as the name suggests, is the type of marketing which is stretched across several countries in the world, i.e. the marketing of products and services is done globally. In this article excerpt you can find the difference between domestic and international marketing in detail.
| Difference between International Marketing and Domestic Marketing | |||||
| Basis | Domestic Marketing | International Marketing | |||
| Definition | “It is concerned with the marketing practises within the researchers or Marketers home country (domestic market).” | “It is the performance of business activities designed to plan, price, promote and direct the flow of a company’s goods and services to consumers or users in more than
one nation for a profit.” |
|||
| Business operation | In a single country | More than one country | |||
| Role of Politics | Political factors are of minor
importance. |
Political factors play a vital role. | |||
| Languages & Cultures | One language and culture. | Many languages and difference in
cultures. |
|||
| Financial Climate | Uniform financial climate. Less Capital is Required | Variety of financial climate. Huge Capital is Required | |||
| Risk Involved | Normal risk is involved. | Higher risks of different nature are
involved. |
|||
| Control of Marketing Activities | Control of marketing activities is easy as compared to international activities. | Control of marketing activities is difficult because of different factors like – regional, cultural, political,
etc. |
|||
|
Government interference |
Less |
Comparatively high |
|||
| Payment | Minimum payment and credit
risks. |
Considerable payment and credit
risks. |
|||
| Familiarity | Well familiarity with domestic market. | Lack of Familiarity with foreign markets, research becomes
Essential. |
|||
| Knowledge
Requirement |
Management knowledge is
required. |
Specific management knowledge
and competence is required. |
|||
|
Use of Technology |
Limited |
Sharing and use of latest techonology. |
|||
| Product Mix | Product mix is decided keeping in view the satisfaction and more
sales. |
Product mix is decided according to foreign market. | |||
| Product Planning and Development | Product planning and development according to domestic market. | Product planning and development according to foreign market. | |||
| Focus | Focus of interest is on general
information. |
Focus of interest is on strategic
emphasis. |
|||
| Market Aspect | Market is much more homogeneous and different
segments. |
Different or diverse markets fragmented in nature | |||
|
Research |
Required but not to a very high level. |
Deep research of the market is required because of less knowledge about the foreign markets. | |||
- What are the different stages of international product life cycle (IPLC)? Explain in detail international product promotion.
International product life cycle:
Product life cycle theory divides the marketing of a product into four stages: introduction, growth, maturity and decline. When product life cycle is based on sales volume, introduction and growth often become one stage. For internationally available products, these three remaining stages include the effects of outsourcing and foreign production. When a product grows rapidly in a home market, it experiences saturation when low-wage countries imitate it and flood the international markets. Afterward, a product declines as new, better products or products with new features repeat the cycle.
General Theory
When a product is first introduced in a particular country, it sees rapid growth in sales volume because market demand is unsatisfied. As more people who want the product buy it, demand and sales level off. When demand has been satisfied, product sales decline to the level required for product replacement. In international markets, the product life cycle accelerates due to the presence of “follower” economies that rarely introduce new innovations but quickly imitate the successes of others. They introduce low-cost versions of the new product and precipitate a faster market saturation and decline.
Growth
An effectively marketed product meets a need in its target market. The supplier of the product has conducted market surveys and has established estimates for market size and composition. He introduces the product, and the identified need creates immediate demand that the supplier is ready
to satisfy. Competition is low. Sales volume grows rapidly. This initial stage of the product life cycle is characterized by high prices, high profits and wide promotion of the product. International followers have not had time to develop imitations. The supplier of the product may export it, even into follower economies.
Maturity
In the maturity phase of the product life cycle, demand levels off and sales volume increases at a slower rate. Imitations appear in foreign markets and export sales decline. The original supplier may reduce prices to maintain market share and support sales. Profit margins decrease, but the business remains attractive because volume is high and costs, such as those related to development and promotion, are also lower.
Decline
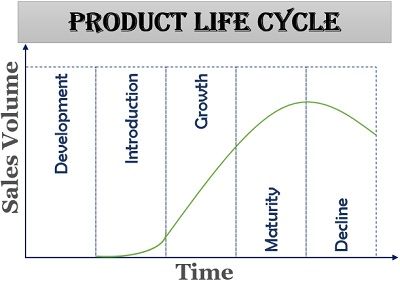
In the final phase of the product life cycle, sales volume decreases and many such products are eventually phased out and discontinued. The follower economies have developed imitations as good as the original product and are able to export them to the original supplier’s home market, further depressing sales and prices. The original supplier can no longer produce the product competitively but can generate some return by cleaning out inventory and selling the remaining products at discontinued-items prices.
International Product Promotion Strategies
Companies develop marketing strategies to build a loyal customer base, to build relationships with those customers and to create value for the customer. Effective product and promotion strategies are essential in making sure your product is readily accessible in the global marketplace. Special considerations are necessary when marketing to global customers such as international issues of technology, transportation and regulation.
Extension
A straight product extension is presenting your product to a global marketplace without any changes. Some products are globally known and need no additional product or promotion changes. People want the product on a global basis, and once it is made available to them, it is purchased without having to create any additional marketing or promotion strategies.
Adaptation
Production and promotion adaptation strategies are used in a global market for a product that may be popular but needs to be adapted to meet local customs and demand. For example, customers of less affluent countries may need a product of similar quality that has been downscaled to be more affordable to purchase. Technology products must be altered to meet the specific language of the country being marketed to.
Invention
Another product and promotion strategy is inventing a new product to meet the needs of a particular country. For example, consumers in crowded commuting conditions might need a laptop product that better fits their travel situation, a more compact version of the typical laptop. This strategy also could take on the form of reinventing a popular product to meet the needs of a particular country or world region.
Pricing Considerations
Global product and promotion strategies must take into consideration the economic conditions of the country where products are introduced. For example, a price that might be discounted in the United States would be considered too high for poorer countries or perhaps not high enough in rich countries. To combat prices being too high in less affluent countries, a company could make a smaller or less complex version at a lower price.
- Role of export marketing in international trade.
ROLE OF EXPORT MARKETING IN INTERNATIONAL TRADE
TRADE Transfer of ownership of goods or services. Trade is sometimes loosely called commerce or financial transaction or barter. INTERNATIONAL TARDE International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders. EXPORT In International Trade, “exports” refers to selling goods and services produced in the home country to other countries. The seller of such goods and services is referred to as an “exporter“. IMPORT In International Trade, “imports” refers to buying goods and services produced in a foreign country to other countries. The buyer of such goods and services is referred to an “importer”. EXPORT MARKETING
Export marketing means exporting goods to other countries of the world as per the procedures framed by the exporting country as well as by the importing country. Export marketing has wider economic significance as it offers various advantages to the national economy. It has bought back several nations back from the dead. DEFINITION According to B. S. Rathor “Export marketing includes the management of marketing activities for products which cross the national boundaries of a country”. “Export marketing means marketing of goods and services beyond the national boundaries”.
FEATURES
- Systematic Process – Export marketing is a systematic process of developing and distributing goods and services in overseas markets. The export marketing manager needs to undertake various marketing activities, such as marketing research, product design, branding, packaging, pricing, promotion
- Large Scale Operations – Normally, export marketing is undertaken on a large scale. Emphasis is placed on large orders in order to obtain economies in large sole production and distribution of goods.
- Dominance of Multinational Corporations – Export marketing is dominated by MNCs, from USA, Europe and Japan. They are in a position to develop worldwide contacts through their network and conduct business operations efficiently and
- Trade barriers – Export marketing is not free like internal marketing. There are various trade barriers because of the protective policies of different countries. Tariff and non-tariff barriers are used by countries for restricting
- Documentation – Export marketing is subject to various documentation formalities. Exporters require various documents to submit them to various authorities like bill of
Need / Importance of Export Marketing at the National Level:
- Earning foreign exchange – Exports bring valuable foreign exchange to the exporting country, which is mainly required to pay for import of capital goods, raw materials, spares and components as well as importing advance technical
- International Relations – Almost all countries of the world want to prosper in a peaceful environment. One way to maintain political and cultural ties and peace with other countries is through international
- Balance of payment – Large – scale exports solve BOP problem and enable countries to have favourable BOP position. The deficit in the BOT and BOP can be removed through large-scale exports.
- Reputation in the world – A country which is foremost in the field of exports, commands a lot of respect, goodwill and reputation from other
- Employment Opportunities – Export trade calls for more production. More production opens the doors for more employment opportunities, not only in export sector but also in allied sector like banking, insurance etc.
Need / Importance of export marketing at Business / Enterprise Level
- Reputation – An organization which undertakes exports can become famous not only in the export markets, but also in the home market. For example, firms like Phillips, , Sony, coca cola, Pepsi, enjoy international
- Optimum Production – A company can export its excess production after meeting domestic demand. Thus, the production can be carried on up to the optimum product
- Spreading of Risk – A firm engaged in domestic as well as export marketing can spread its marketing risk in two parts. The loss is one part (i.e. in one area of marketing) can be compensated by the profit earned in the other part /
- Higher profits – Exports enable a business enterprise to earn higher prices for goods. If the exporters offer quality products, they can charge higher prices than those charged in the home market and thereby raise the profit
CHALLENGES TO EXPORT MARKETING
- Technological differences- The developed countries are equipped with sophisticated technologies less developed countries, on the other hand, lack technical knowledge and latest equipments.
- Reduction in export Incentives– Over the years, the Govt. of India has reduced export incentives such as withdrawal of income tax benefits for majority of exporters. The reduction in export incentives de-motivates exporters
- Several competitions in global marketing– Export marketing is highly competitive. Indian exporters face three-faced competition while
- Problem of product standards– Developed countries insist on high product standards from developing countries like India. The products from developing countries are subject to product tests in the importing
- Problem in preparing Documents– Export involves a large number of documents. The exporter will have to arrange export documents required in his country and also all the documents as mentioned in the documentary letter of credit. In India, there are as many as 25
IMPORTANCE OF EXPORT MARKETING
- Increased Sales and Profits. Selling goods and services to a market the company never had before boost sales and increases revenues. Additional foreign sales over the long term, once export development costs have been covered, increase overall
- Enhance Domestic Competitiveness Most companies become competitive in the domestic market before they venture in the international arena. Being competitive in the domestic market helps companies to acquire some strategies that can help them in the international
- Gain Global Market Shares. By going international companies will participate in the global market and gain a piece of their share from the huge international
- Selling to multiple markets allows companies to diversify their business and spread their risk. Companies will not be tied to the changes of the business cycle of domestic market or of one specific country.
- Lower Per Unit Costs. Capturing an additional foreign market will usually expand production to meet foreign demand. Increased production can often lower per unit costs and lead to greater use of existing
- Explain the concept of Internal Marketing. Also describe international marketing Strategies.
Internal marketing is the promotion of a company’s objectives, products and services to employees within the organization. The purpose is to increase employee engagement with the company’s goals and fostering brand advocacy.
Employees who are enthusiastic about their company and its offerings are likely to share that enthusiasm with their social networks. As a result, internal marketing can be an effective part of external branding and marketing efforts. However, internal marketing can only go so far since an employee’s attitude toward the organization is affected by every element of that individual’s experience working for the business. Keeping employees happy and engaged is important to external marketing efforts as well.
Common internal marketing efforts include:
- Ensuring that all employees know that their contributions are essential to the company’s success.
- Educating all employees about the company’s products and services.
- Reinforcing the concept that customers are, when all is said and done, the source of employees’ salaries.
- Providing adequate salaries and benefits, plus a pleasant work environment.
- Encouraging employee input on corporate policies, management and operation – including criticism.
- Acting on employee suggestions that have merit and publicly acknowledging the value of the input.
- Confirming that the corporate mandate and objectives are clearly described and disseminated throughout the organization.
- Providing opportunities for advancement, professional development and promotion.
- Ensuring that the corporate culture is consistent with work-life balance.
- Fostering communication and collaborationamong employees through various methods from formalized settings and to casual areas for gathering, such as lounges.
Internal marketing operates on the idea that customer opinions of a company are based on their experiences with the business, not just with the products. By treating employees as “internal customers”, internal marketing helps employees align with the company’s vision and operations. In turn, they provide their customers with a consistent and valuable experience. Internal marketing campaigns are often lead by a company’s human resources department, which is responsible for distributing information and providing training on the company’s objectives and strategies.
International Marketing Strategies
Marketing can be defined as a process of creating, delivering and communicating the value of a product or service by an organizational function to the customers for the purpose of selling the product or service in ways that also benefit the organization and its shareholders. In international marketing, also known as global marketing, the organizations find out the needs of the customers in foreign countries so that marketing is carried out across the national borderlines for providing the sustomers the required entities at right place and at the right time. In this strategy the organizations adopts techniques that are the extensions used in the home country. It includes market identification and market targeting, selection of entry mode, marketing mix decision and strategic decisions in order to compete in the international markets.
When creating a worldwide marketing plan, every organization needs to formulate its international marketing strategies. It involves a five step procedure. This includes market assessment product strategy, price strategy, place strategy and promotion strategy. The factors to be considered while formulating an international marketing strategy are briefly discussed below:
Market Assessment
This include a five step screening procedure:
- The first step is the identification of the customers’ needs and to list out the items.
- After listing out the basic items, the list is shortened in the next step by screening by analyzing the financial and economic condition of various potential markets.
- Under the third steps, before entering any potential market the organization considers the legal and political forces of the host country.
- In the similar way, under the fourth step also the organizations should consider the socio-cultural forces of potential markets.
- If the organization finds a choice between two or more countries, then at the fifth step they should consider the markets where the competitions are less.
After all the screening steps, in the final selection the organization arranges trips to the actual locations where their executives can evaluate the potential markets for providing overseas goods and services.
Product strategy
Product strategy varies depending on the goods and the customers. To sell a particular product in a country some modifications are required in the product or its marketing strategy according to the requirements of the market.
Pricing Strategy
To price a product depend on many factors like the cost of raw materials, cost of developing the product, cost of transportation of the product etc. while pricing product government regulations, legal forces are also some of the limiting factors.
Place Strategy
While selling a product the multinational organizations should keep in mind to choose a place that is most convenient for the customers. To distribute the product so that it reaches the customers the organizations should fix proper distribution channels. The manner, by which the product is distributed, on the other hand, is influenced by the competitions in the market for similar types of product.
Promotion strategy
To stimulate the demand of a particular product or a service, a company adopts many strategies to attract the customers. Some strategies may be through advertisement and personal selling. By adopting such strategies multinational enterprises promote their goods and services in different countries.
Types of International Marketing Strategies
- Individualized Marketing Strategy
Individualized marketing, as its name suggests, focuses each and every targeted market in detail which requires the company to gather an extensive amount of research data. Therefore, to maintain the balance between the profit and the costs involved in that research, the focus is kept to, just, two or three countries. Furthermore, a revised version of the product is created to match the needs of all the individual markets by keeping economic, political and social factors in the notice.
- Global Marketing Strategy
Promoting a brand globally enables it to create a unified version of the product by ignoring most or nearly all of the differences between different countries is known as global marketing. Application of such international marketing strategies takes place just because of the reason that the world is now acting like a global village where customers are having a standardized taste and their ideas of assessing a product are getting more and more similar. This strategy cuts the costs of research significantly, but promotion needs enormous efforts to get the word for your product deep down in the markets.
These international marketing strategies are also known as Global Marketing Strategies and almost used in all over the world as marketing product or brand globally.
Tools for International Marketing Strategies
Even though the market gets bigger and bigger as the number of targeted countries increases, but the tools used for promotion are same.
- Advertisements
One of the most powerful marketing tools that can help you achieve your dream of converting your product to sales is advertising it through different means. Put the word for your product in international newspapers, radio channels, anything that can get a poster on it and most importantly, the Internet because it houses hundreds of other means of marketing your brands like emails, websites, and many others. Furthermore, you can also run a contest for which entrants will have to share the news about your brand to their friends and family.
- Price Promotions
The best way to get a buzz of the product is by putting up some promotions. Either you can give your product sales a huge boost through discounts or by giving your customers some timed trial or you can couple up your product with a freebie for every purchase.
- Make use of tradeshows
There are many types of products that customers do not buy until they have tested by themselves especially cars. Actually, they are looking for the experience of the product to be purchased and that’s where tradeshows come into play. The company invites its customers to the trade show and let them experience the full potential of the brand.
- B2B Marketing
B2B is an unusual tactic often used by bigger enterprises is to spread the word among individuals and organizations alike which allow them to sell their product to other commercial businesses, institutions, and other agencies, which can then either use this product or resell it.
- Inbound marketing
Making use of the requests, for the new products, often made by the customers can undoubtedly lead to additional sales of services that you currently have. For example, when a customer contacts the bank to check the account balance, the bank’s contact center takes advantage of the chance and offers its customers to apply for any other service.
- Outbound marketing
Reaching out to individual target groups is a lot more fruitful than addressing the whole world, since it lets the potential customers know that a particular business exists and can be a lot more advantageous to our cause. For this purpose, a list of prospects is developed that can provide a starting point for the brand and this list is, then, further refined to concentrate the search for new customers. The same was the case of Microsoft when it spread the word of its accounting software.

